The terms allergy, intolerance, anaphylactic, and hypersensitivity are thrown around quite a bit in the Gutsy community, so I wanted to give a breakdown of them today to help you understand more. Namely, an IgE vs IgG allergy.
Starting with IgE vs IgG, we could get super detailed and medical.
I could go into all the nooks and crannies, likely far more than will ever truly be helpful for you.
But I won’t because of just that, I want to be truly helpful, so my goal here is to keep the information simple and digestible (pun intended – yes).
In case you want the super detailed, complex information, you’ll find it HERE.
Like this:
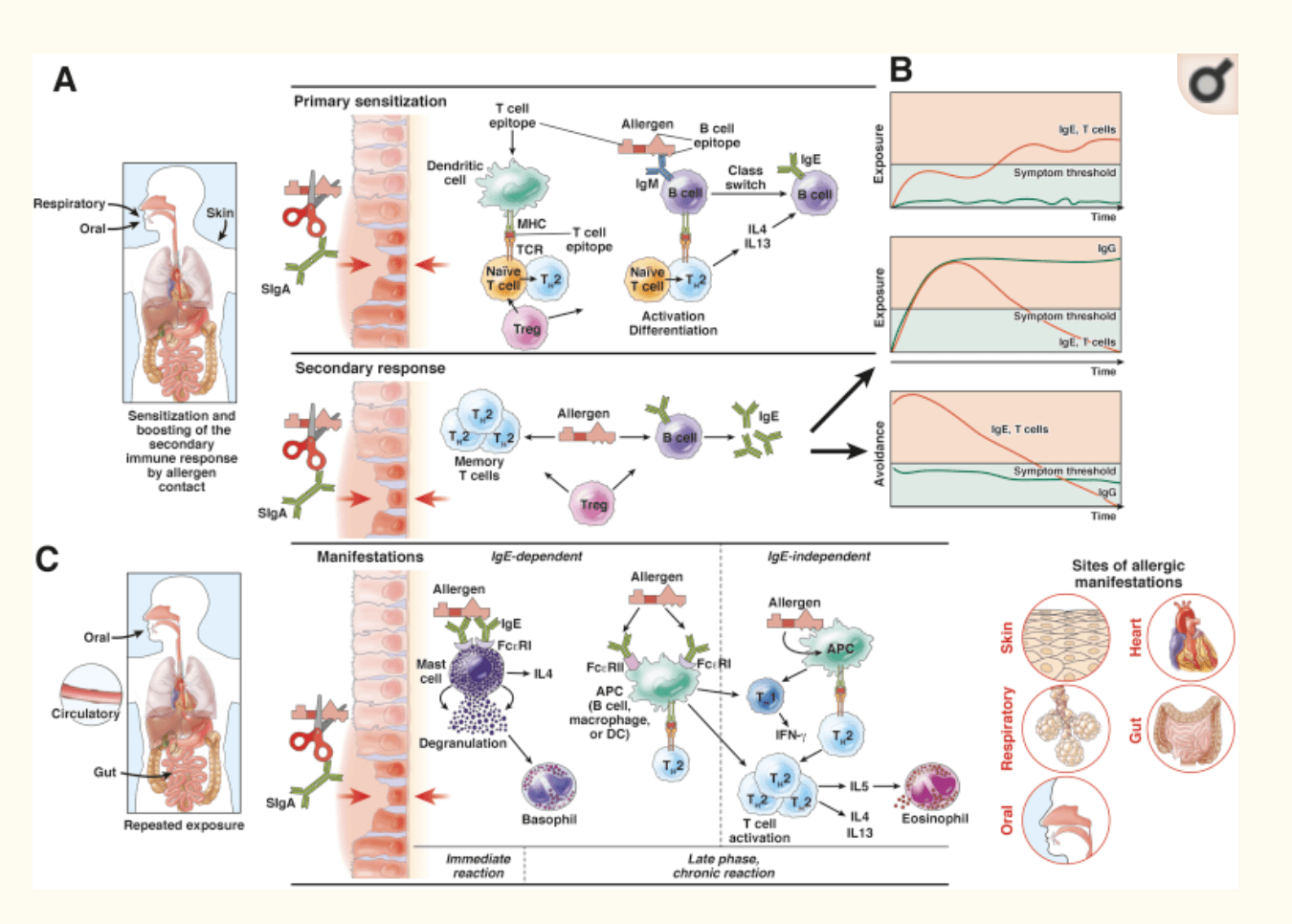
IgE vs IgG
Click HERE to save this post for later.

To understand it in the most simplistic way:
immediate allergy (IgE hypersensitivity reaction) vs. delayed allergy (IgG delayed hypersensitivity reaction)
The “Ig” stands for Immunoglobulins, and there are five major kinds of immunoglobulins: A, D, E, G and M. They are special proteins produced by the body in response to foreign substances including bacteria and viruses.
Today we are only focusing on the “E,” and “G,” but for reference:
A:
One of the most common; it is mainly present in body secretions and is the chief antibody in the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tract and in saliva and tears.
D:
Is present in small amounts in serum and is thought to function in certain allergic responses.
M:
Is a large molecule; found in blood and is involved in combating blood infections. It is the first or primary immunoglobulin produced following exposure to an antigen.

IgE
IgE stands for Immunoglobulin E and they are antibodies produced in the immune system.
If you have an allergy, your immune system overreacts to an allergen by producing antibodies called Immunoglobulin E (IgE).
These antibodies travel to cells that release chemicals, causing an allergic reaction. This reaction usually causes symptoms in the nose, lungs, throat, or on the skin.
Each type of IgE has specific “radar” for each type of allergen. That’s why some people are only allergic to cat dander (they only have the IgE antibodies specific to cat dander); while others have allergic reactions to multiple allergens because they have many more types of IgE antibodies. (source)
Symptoms of IgE Reaction
Click HERE to save these for later.

- Periodic or persistent itching
- Hives
- Itchy eyes
- Eczema
- Nausea, vomiting, persistent diarrhea
- Sneezing, coughing, congestion
- Difficulty breathing
- Asthma symptoms: wheezing, breathlessness, coughing, tightness in the chest
(source)
IgG
igG stands for Immunoglobulin G and it is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation.
It has 4 different subclasses, IgG1-4.
IgG is always there to help prevent infections.
It’s also ready to multiply and attack when foreign substances get into the body.
When you don’t have enough, you are more likely to get infections. (source)

Looking to support your immune system and promote a healthy immune response? Tummy Soothe is an absolute game-changer for support of both the immune system and overall digestive function. It contains ImmunoLin, a dietary supplement that contains both immunoglobulins and other compounds to promote healthy gut lining cells.
Use code AGUTSYGIRL at checkout to save 15% off Tummy Soothe.
Tummy Soothe with IGG can help discourage immune system flare ups and prevent some of the symptoms associated with food intolerances.
Why ImmunoLin®?
For the Gutsy community, if you simply understand the above and what ImmunoLin® is, it’s fairly easy to see why I’m such a fan.
But, let me give you 3 more reasons for why:
- ImmunoLin® binds to microbial antigens, including lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which helps to limit antigen absorption.
- Speaking of things ImmunoLin® binds to, check out the all the things it binds to below! Incredible, right?!
- It supports intestinal homeostasis, which refers to the overall “balance” of a functioning, healthy intestinal tract, and is critical for optimal nutrient utilization and immune function.
SBI Binding Agents
If any of these are of concern to you, then Tummy Soothe is for you, as SBI binds to the following antigens:
- Aflatoxin B2
- Aflotoxin G1
- C. albicans lysate
- C. albicans Als3 protein
- H. pylori CagA protein
- Cytolethal distending toxin subunit A
- Cytolethal distending toxin subunit C
- Shiga-like toxin type 1
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
- C. difficile Toxin A & B
- Peptidoglycan
- Flagellin
- Zymosan
- C-di-AMP
- CpG
- MDP
- Gliadin
- E. coli
- Staphylococcus
- Klebsiella Pneuomonia
- Salmonella Typhimurium
- Serratia Marcescens
Symptoms of IgG Deficiency
Click HERE to save these for later.

Infections that most often affect people with IgG deficiency are:
- Sinus infections and other respiratory infections
- Digestive tract infections
- Ear infections
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Infections that result in sore throat
- Severe and life-threatening infections (rare)
- In some people, infections cause scarring that harms the airways and how the lungs work. This can affect breathing. People with IgG deficiency also often find that pneumonia and the flu vaccines don’t keep them from getting these infections.
(source)
Food Related
In the Gutsy community, most of you want to know the correlation between all these terms and food.
And as I mentioned in the beginning, the terms allergy, intolerance, anaphylactic, and hypersensitivity are thrown around quite a bit. It can be confusing to differentiate between these words, but knowing the difference is VERY important.
Broken down, here are the terms (as they relate to food):
Food Allergy
A food allergy is an “immune system reaction that occurs soon after eating a certain food. Even a tiny amount of the allergy-causing food can trigger signs and symptoms such as digestive problems, hives or swollen airways.”
It may or may not cause an anaphylactic reaction.
The most common food allergy signs and symptoms include:
- Tingling or itching in the mouth
- Hives, itching or eczema
- Swelling of the lips, face, tongue and throat or other parts of the body
- Wheezing, nasal congestion or trouble breathing
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or fainting
IGG food allergies often include immediate responses and symptoms to a food and are much more dangerous than food sensitivities.
It is important to get checked for food allergies if you are experiencing any of these symptoms.
Some of the top IgE food allergies include:
- dairy
- eggs
- fish
- shellfish
- soy
- wheat
- soybeans
Food-Induced Anaphylaxis
Food-induced anaphylaxis is a, “leading cause of anaphylaxis treated in emergency departments and hospitals around the world.
Peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish are the most commonly implicated foods.
Food-induced anaphylaxis may occur in any age group and with any food. However, food-induced anaphylaxis fatalities disproportionately affect adolescents and young adults with peanut and tree nut allergy.
Individuals who have both IgE-mediated food allergy and asthma are at a higher risk for food-induced anaphylaxis fatality.”
Anaphalytic reaction signs and symptoms include:
- Constriction and tightening of the airways
- A swollen throat or the sensation of a lump in your throat that makes it difficult to breathe
- Shock with a severe drop in blood pressure
- Rapid pulse
- Dizziness, lightheadedness or loss of consciousness
Emergency treatment is critical for anaphylaxis. Untreated, anaphylaxis can cause a coma or even death. (source)
Food Intolerance and Hypersensitivity
Yes, these two are basically the same thing.
“Food intolerance, also known as non-IgE mediated food hypersensitivity or non-allergic food hypersensitivity, refers to difficulty in digesting certain foods.”
A food intolerance and hypersensitivity will not trigger an allergic reaction.
However, it can cause a whole host of unpleasant symptoms such as abdominal pain, gas, bloating, headaches, and heartburn.
A food intolerance occurs when the digestive system fails to break down certain foods. It often can be due to a lack of pancreatic enzymes or certain developments over time, such as a lactose intolerance.
It also is often linked with increased iGg proteins, which can trigger an overactive immune response. This can cause inflammation and discomfort, especially in the gut region.
Food intolerances are extremely commonly, and it is where the majority of the Gutsy community falls. And while it’s not life-threatening, it’s frustrating because a food intolerance has a delayed response.
It can take anywhere from hours to days to show up after eating specific foods.
Thus, people tend to spin their wheels for years trying to figure out what’s wrong. Some even go their entire lives without pinpointing which specific foods are giving them issues.
This is why I created a gut healing journaling SYSTEM – to help those of you in this category.
The PDF version can be instantly downloaded HERE.
There is also a physical journal.
Elimination Diet
An elimination diet can be one of the best ways to figure out food sensitivities without getting tested.
Sensitivity to a specific food can be found by eliminating all common sources of inflammation and then slowly adding them back in. Slowly is key here due a delay reaction.
If you don’t want to go for the full elimination diet, you can start by simply eliminating some of the most common food sensitivity items.
These include:
Dairy
Lactose intolerance is one of the most prevalent kinds of food intolerances that occurs due to insufficient levels of enzymes. These enzymes, known as lactase, are specifically meant to break down sugars that are found in milk.
Common reactions with an intolerance to dairy includes skin breakouts, GI symptoms, and respiratory symptoms.
Gluten
Gluten is another extremely common food intolerance that occurs due to the inability to properly digest the proteins that form gluten. This is often referred to as a non-celiac gluten sensitivity, as it is not an autoimmune disease. (Celiac disease is an autoimmune disease where the consumption of gluten leads to the damage of the small intestine.)
Gluten intolerance often causes primarily digestive concerns, and is thought to be one of the root causes of IBS. Opting for a gluten-free diet is one of the best places to start in any elimination diet.

Caffeine
Believe it or not, but caffeine is another food intolerance that many people have. While this one may be slightly harder to remove, it could be extremely beneficial if you find it is causing you issues.
Shellfish
Shellfish is another one that may cause digestive upset if consumed. This is very different from an allergic reaction, where your immune system will cause allergy-like symptoms.
Peanuts
Peanuts can cause both respiratory and digestive concerns if someone is intolerant to them.
Corn
Corn is one of the most common food sensitivities and has been linked with IBS symptoms such as abdominal pain, gas, and bloating.
Soy
Some people are sensitive to this legume and will show signs of GI distress.
Histamines
Some individuals are also sensitive to high levels of histamines due to the presence of too much histamine already in their bodies.
The release of histamines triggers mast cells, which are a type of immune cells that send the immune system into action.
This can cause both allergy-like symptoms as well as GI issues, and dizziness.
Foods high in histamine include alcohol, fermented foods, dried fruits, processed meats, and shellfish.
If you want an extended histamine list click HERE.
By eliminating these common foods, you may find some relief in your symptoms.
If you add them back in one by one, you should be able to pinpoint some of the problematic sources.
Leave at least 3 days in between adding each food back in, in order to account for the delayed appearance of symptoms.
It may be helpful to keep track of all skin, respiratory, and gastrointestinal symptoms over this time period in order to remain organized.
Hint: the journal helps you do this!
Testing
Click HERE to save these for later.

There are many different ways to go about IGG testing, depending on your signs and symptoms.
If you feel it’s an allergic and/or anaphylactic reaction, head to the doctor immediately for urgent care.
Otherwise, here are several testing options that can be considered:
- Skin testing
- Blood testing
- Lung function testing
- Food challenge
- Drug/medication challenge
- Aspirin desensitization
- Patch testing
- Food Sensitivity Health Tests from Home (or via your doctor’s office)
- FoodMarble AIRE device [(code GUTSYG to save 20% off your device)]
(source)
Note: because I had so many symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease – even in the very beginning of my journey – here are all the tests I have personally done over the years: skin testing, blood testing, food challenge, patch testing, food sensitivity testing and the FoodMarble AIRE device (yeah, most of them)!
Food Sensitivity Testing
Food sensitivity testing is one of the best places to start for anyone with Gutsy issues, as it can be an underlying issue behind your symptoms.
Most food sensitivity tests measure IgG antibody levels associated with different foods and can show you which ones you may be having issues with.
While these are not 100% accurate and can give false positives (I think that’s mostly due to leaky gut syndrome), they can give you a solid foundation for where to start in remapping your diet.
Most tests take a blood sample and analyze these for the presence of elevated IgG levels, which may indicate some sort of sensitivity.
The test results take a few days to a couple of weeks to get back, so it is a fairly quick turn-around.
Allergy Testing
A true food allergy test includes skin prick testing. This exposes your skin to a particular antigen and then measures the allergen-specific IgE in your bloodstream.
This is extremely important if you feel like your symptoms more closely resemble an immune system response vs. than food sensitivity reactions.
Food Sensitivity vs. Allergy
If you are having trouble differentiating if your reaction is a food sensitivity or an allergy, here are some questions to ask yourself.
How soon after eating do I experience symptoms?
Oftentimes an allergy will create an immediate reaction, while a food intolerance takes longer to notice – a delayed reaction.
What symptoms am I experiencing?
If your symptoms are more closely related to respiratory issues, than I would be more inclined to look for IgE reactions.
This indicates an allergy rather than a food sensitivity.
How much of the food causes a reaction?
If even a small bit of food is causing a reaction, then it is most likely an allergy.
While some people may be EXTREMELY sensitive to a certain food, most food intolerances occur after eating a sizable amount.
Understanding where you (or your Gutsy Child) falls is really the first step in getting the problem under control.
While IgE vs IgG are different, they both pose many problems and are a beast to deal with in the Gutsy community.
p.s. This is just scratching the surface of topics and issues relating to all of the above. If you have specific questions around any of them, please CONTACT ME so that I can do follow-up, detailed posts.
Or better yet, join Gut Healing: ELEVATED to get your questions answered today!
If you liked this post, you might also enjoy:
- Reasonable SIBO
- Interesting Facts About the Immune System {Plus 13 Science Backed Ways to Boost Your Immune System}
- ImmunoLin as the Star Ingredient in Tummy Soothe, My Obsession Explained (Episode 105 with Brian Kaufman)
Xox,
SKH
🤰 bloating be gone! weight loss through optimal gut health for women
💃ʜᴇᴀʟ ʏᴏᴜʀ ɢᴜᴛ. ʜᴇᴀʟ ʏᴏᴜʀ ʟɪfe.
🫶🏻 founder gutbyome.com






Thank you for sharing this! While being treated for Sibo, they discovered I had EoE and Mast Cell Activation. 2 autoimmune diseases, that I know for a fact happened because of stree and a bad gut for too long! They also discovered, by way of the most humiliating tests, that I have pelvic floor prolapse ( Straining for too many years with Sibo C) . I’m 44. Now having a surgery too. Just saw an allergist and he is having me do no dairy, as well as put me on a stupid high dose of a PPI. New scope in 4 weeks. I had a couple of test come back that were noted with these as abnormal, so the article was very helpful! Do you know anything about Prostoglandin D2? Mine was 163 pg/ml. Gut health and stress management are so key to a healthy life! I’m trying to find my way back…
Hi! Thanks for sharing. I don’t know much about Prostoglandin D2, sorry. I’ll be thinking of you.
Thanks for your article. I’ve been having digestive issues and recently went to my doctor and was tested using the IGE method and found out I have a mild allergic to cow’s milk and shrimp. I ordered the everlywell test (IGG) and am interested in the findings. Thank you for this article explaining the difference.
Hi Malinda! Looking forward to hearing the results!