Let’s chat about the endocannabinoid system and your gut today.
I recently went into our local CBD center because I wanted to learn more. Upon entering, I saw this graphic.
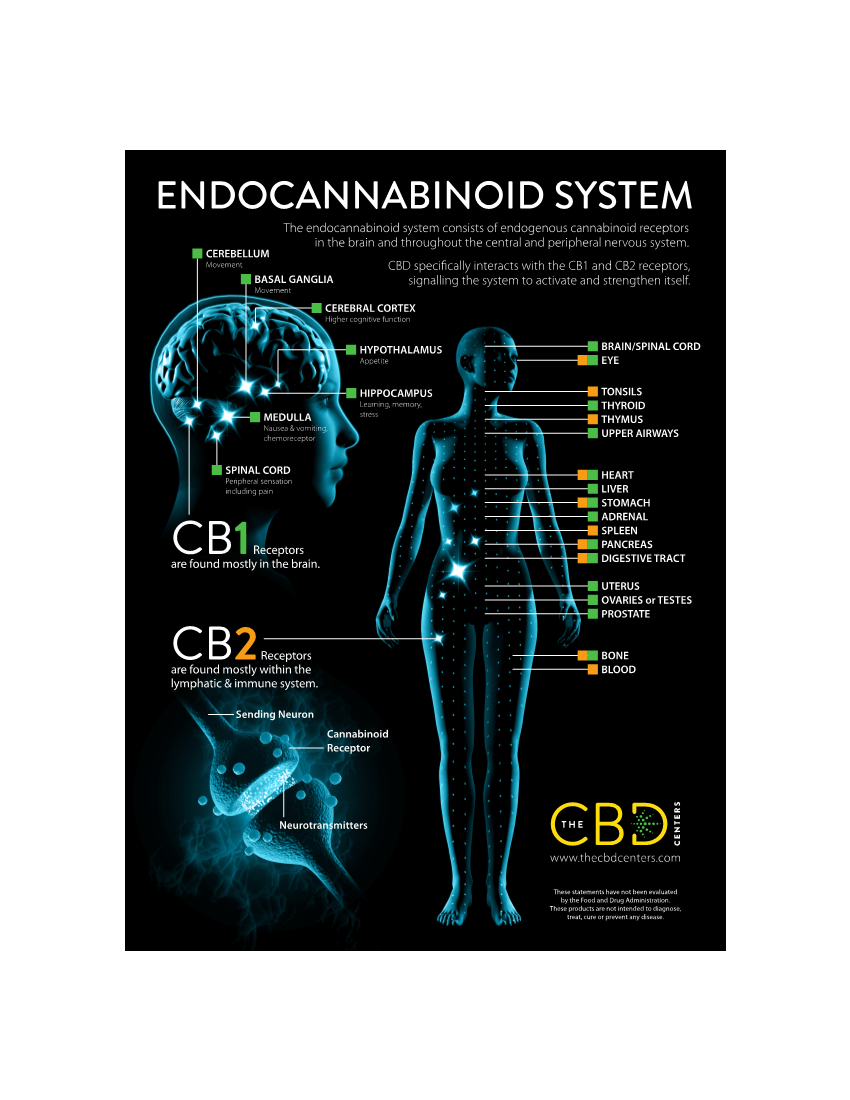
And I started asking questions because I was fascinated.
Now, before I continue on, I want to make a few things clear:
- My local CBD Center is THIS one.
- Though I have posted one CBD post on here before, CBD for Digestion, I didn’t personally write it. Highly recognized nutritionist, Ashley Koff did.
- I’m interested in learning even more about CBD and its implications on the digestive system. I also want to learn more about the CBD products I have access to locally.
With that, let’s start with the basics.
What the Heck is an Endocannabinoid?
All mammals have endocannabinoids.
The difference is whether it is produced in the body (cannabinoids) or by the plant, phytocannabinoids (Cannabis). There are also synthetic ones (Synthetic Cannabinoids).
Note: The discovery of phytocannabinoids helped lead to the discovery of the endocannabinoid system (discussed below).
There are two endocannabinoids: anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, or 2-AG. Endocannabinoids are cannabinoids that are naturally produced in the body by the brain. This makes sense as endo means “internal, within.”
Endocannabinoids then bind to cannabinoid receptors on target cells throughout the body.
Cannabinoid Receptors
If you look at the image above, you’ll see CB1 receptors (in green) and CB2 receptors (in orange).
When cannabinoids bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors, they act to change the way the body functions.
CB1 receptors (mostly in the brain).
- CB1 receptors help to mediate inhibition of neurotransmitter release
- They are some of the most widely expressed G protein-coupled receptors in the brain.
- You’ll find them at the terminals of central and peripheral neurons and areas of the brain. They control movement and postural control, pain and sensory perception, memory, cognition, emotion, autonomic and endocrine functions
- They are also found in other parts of the body including the heart, uterus, testis, small intestine and peripheral cells
- Most recently, CB1 has been isolated in tissues that are important for energy metabolism such as the liver, adipose (fat) tissue and skeletal muscle.
CB2 receptors (throughout the lymphatic and immune systems).
- CB2 receptors are predominantly expressed in the cells of the immune system both within and outside the central nervous system such as the spleen, T-cells, B-cells and macrophages.
- They were identified in 1993 through homology cloning.
- They work to modulate modulate cytokine release and immune cell migration in a manner that seems to reduce inflammation and certain kinds of pain.
You’ll find these endocannabinoids (naturally produced in the body by the brain) in the endocannabinoid system.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
Discovered only about 30 years ago, the Endocannabinoid System is relatively “new.”
The NIH states,
The endogenous cannabinoid system—named for the plant that led to its discovery—is one of the most important physiologic systems involved in establishing and maintaining human health. Endocannabinoids and their receptors are found throughout the body: in the brain, organs, connective tissues, glands, and immune cells.
With its complex actions in our immune system, nervous system, and virtually all of the body’s organs, the endocannabinoids are literally a bridge between body and mind. By understanding this system, we begin to see a mechanism that could connect brain activity and states of physical health and disease.
The ECS (Endocannabinoid System) role is to keep our other body systems in check, to maintain homeostasis (biological harmony in response to changes in the environment).
According to Thorne,
It can readily be viewed as the body’s internal adaptogenic system, constantly working to maintain a vast range of functions in equilibrium. Endocannabinoids broadly work as neuromodulators and, as such, they regulate a wide scope of physiological processes – from fertility to pain.
Okay, so now that the basics have been discussed you are thinking, “Great, but what does this have to do with my gut?”
Endocannabinoid System and Your Gut
Click HERE to save this post for later.
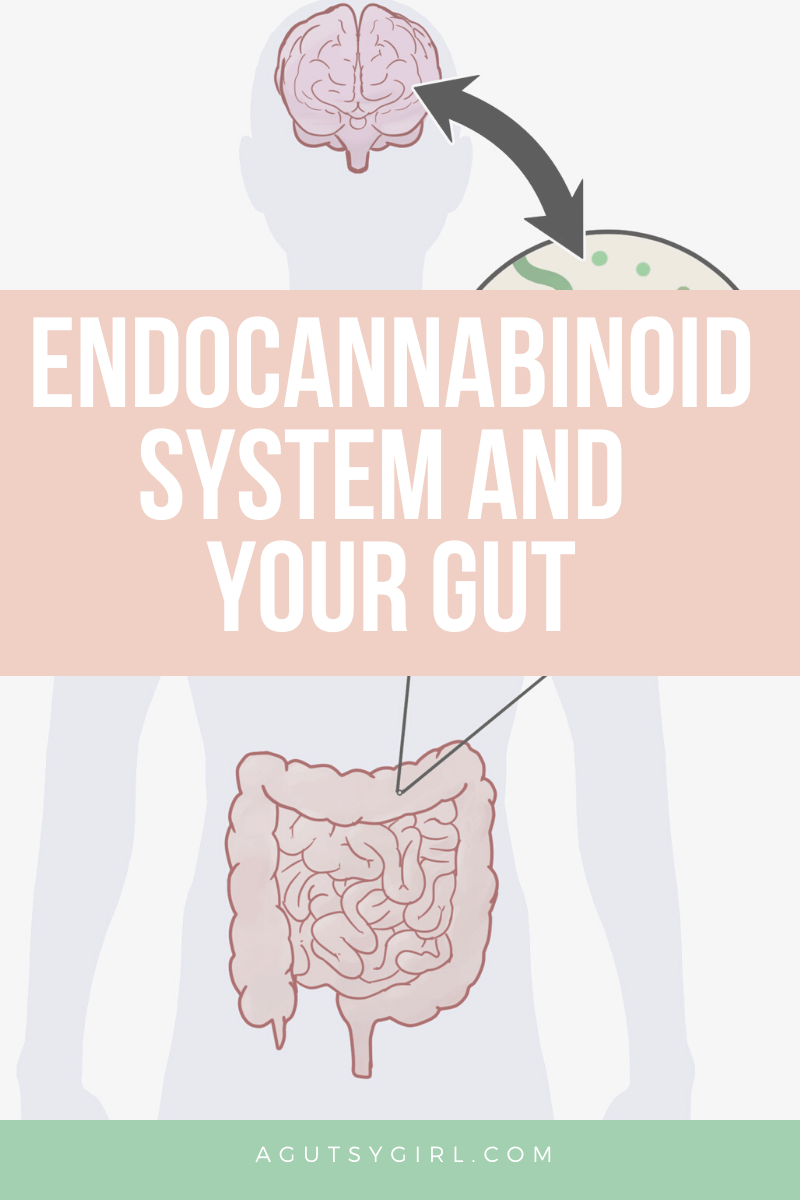
Let’s first refer back to the graphic. According to the graphic, the digestive tract contains both CB1 and CB2 receptors, as does the stomach.
And, according to Thorne,
It is believed that the ECS might be the “missing link” in explaining the gut-brain-immune connection that plays an important role in the functional health of the digestive system.
The ECS is a regulator of gut immunity, possibly by limiting the immune system from destroying healthy flora, and also through the modulation of cytokine signaling.
The ECS modulates the natural inflammatory response in the digestive system, which has important implications for a broad range of health concerns. Gastric and overall GI motility also seems to be partly regulated by the ECS.
More research on the endocannabinoid system and your gut:
- The ECS is involved with digestive motility, nausea, intestinal inflammation, gut permeability, cancer cell proliferation, and complex interactions with probiotic bacteria of the intestines.
- An extensive amount of research is now linking the endocannabinoidome to intestinal health through fascinating mechanisms that include endocannabinoid receptor expression in the gut and interplay with the intestinal microbiota. A dysregulated endocannabinoid system may lead to inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer.
- The ECS is ubiquitously expressed in the human body and it actively controls gut homeostasis.
- CB1 has been found in intestinal epithelial and in the enteric nervous system (ENS).
- CB2 has been found on enteric neurons but it is predominantly expressed by intestinal immune cells.
- The gut and brain communicate with each other, mostly via the vagus nerve, but also via the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS).
- In rats, fasting increases the small intestine’s production of the endocannabinoid anandamide (known as the “bliss molecule” for its powerful effect on mood).
Is this all as fascinating to you as it is to me?

Full Spectrum CBD Tincture
As part of my never-ending quest to have the strongest gut on the planet (only kind of kidding), I have added in this full spectrum CBD tincture. It’s the natural-flavored, 1500 mg option. But there are also these:
For a multitude of reasons, this one is top-notch. You don’t even have to live in the small town where I live to purchase it, either. All the links above will allow you to purchase and have it shipped directly to you.
With so many CBD oils on the market now, it’s so hard to know which one to choose and why.
Alright, this post is already super long, so I’ll be back soon to share more about all of that.
Sources: HERE, HERE, HERE, HERE, HERE, and HERE.
If you liked this post, you might also enjoy:
- Peek Into My Personal Onegevity Microbiome Report and Review
- The Gut-Brain Connection
- The Gutsy Girl’s Bible: an approach to healing the gut
Xox,
SKH
🤰 bloating be gone! weight loss through optimal gut health for women
💃ʜᴇᴀʟ ʏᴏᴜʀ ɢᴜᴛ. ʜᴇᴀʟ ʏᴏᴜʀ ʟɪfe.
🫶🏻 founder gutbyome.com